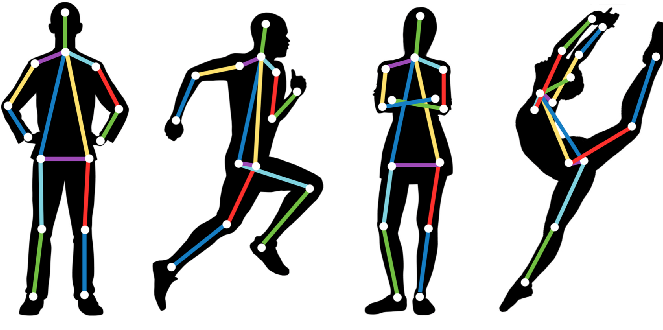
In the realm of artificial intelligence and computer vision, pose estimation machines are making significant strides, revolutionizing how humans interact with computers and the digital world. This innovative technology enables machines to understand and interpret human ai pose detection, unlocking a wide array of applications across various industries.
What is Pose Estimation?
Pose estimation refers to the computer vision technique that can detect and track the position and orientation of a person’s body, limbs, and joints in real-time from images or video. This technology essentially allows computers to understand the spatial positioning of a person’s body, enabling them to interpret gestures, movements, and even predict intentions.
How Pose Estimation Machines Work
Pose estimation machines typically use deep learning models, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), to analyze visual data. These models are trained on vast datasets of images and videos that contain human poses in various environments and conditions. The key steps involved in pose estimation include:
- Detection: Identifying the presence of humans in an image or video frame.
- Localization: Estimating the location of key body joints such as shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, knees, and ankles.
- Tracking: Continuously predicting and updating the positions of these joints over time.
Advanced pose estimation systems can handle complex poses and movements, even in crowded or challenging environments, making them versatile tools for a wide range of applications.
Applications of Pose Estimation Machines
The applications of pose estimation machines span several domains, each leveraging the technology in unique ways:
- Healthcare: Assistive technologies for rehabilitation and physical therapy, monitoring patient movements, and posture.
- Sports and Fitness: Analyzing athletic performance, providing real-time feedback on posture and technique.
- Retail and Advertising: Customer behavior analysis, interactive shopping experiences.
- Gaming and Entertainment: Gesture-based controls, immersive virtual reality experiences.
- Security and Surveillance: Monitoring suspicious activities, detecting anomalies in public spaces.
- Education: Interactive learning tools, virtual classrooms.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its rapid advancements, pose estimation technology faces several challenges, including occlusion, variability in human poses, and real-time processing requirements. Researchers are continually working on improving the accuracy, robustness, and efficiency of pose estimation algorithms.
Looking ahead, the future of pose estimation machines is promising. As AI and computer vision technologies evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated systems that can accurately interpret and respond to human movements and gestures in real-time, further blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds.